Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
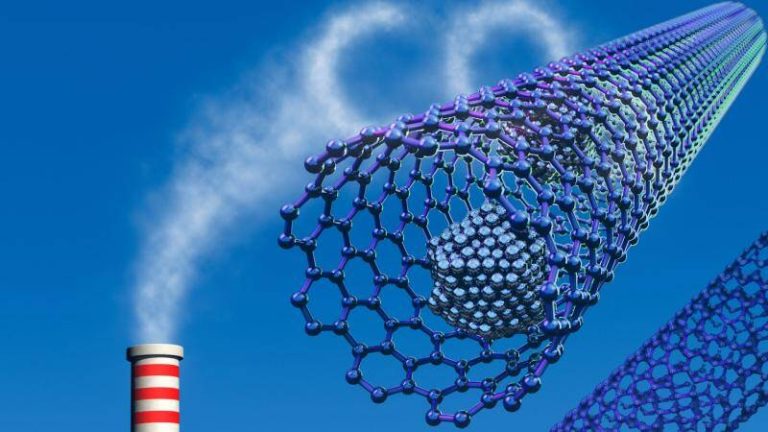
The pursuit of clean energy and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions has become a pressing concern globally. One of the key strategies to combat climate change is the development of efficient carbon capture and storage technologies. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as promising materials for this purpose, owing to their high surface area and tunable properties. However, the traditional synthesis methods for MOFs often involve the use of toxic hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant environmental and health risks. In a breakthrough development, researchers have now devised a fluoride-free synthesis method for MOFs, replacing hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators. This innovative approach not only simplifies the production process but also yields superior crystals that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature.
The new synthesis method has far-reaching implications for the development of affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems. By leveraging the enhanced gas capture capabilities of MOFs, these technologies can play a crucial role in mitigating climate change globally. The simplified and safer production process is expected to accelerate the widespread adoption of MOF-based solutions, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
The limitations of traditional MOF synthesis
Traditional MOF synthesis methods typically involve the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic and corrosive substance. The handling and disposal of hydrofluoric acid pose significant risks to human health and the environment, making it an undesirable choice for large-scale industrial applications. Furthermore, the use of hydrofluoric acid often results in the formation of defects and impurities in the MOF crystals, which can compromise their gas capture efficiency.
In contrast, the new fluoride-free synthesis method utilizes safer modulators to direct the formation of MOF crystals. This approach enables the production of high-quality crystals with minimal defects, leading to enhanced gas capture capabilities. The simplified process also reduces the production costs and environmental footprint of MOF synthesis, making it an attractive option for industrial-scale applications.
Superior gas capture capabilities
The MOF crystals produced using the new synthesis method have demonstrated superior gas capture capabilities, particularly for carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The high surface area and tunable properties of MOFs enable them to selectively trap greenhouse gases, making them ideal for carbon capture and storage applications. The enhanced gas capture efficiency of the new MOF crystals can be attributed to the reduced defects and impurities, which allow for more efficient gas molecule interactions.
The ability of MOFs to store hydrogen at room temperature is also a significant advantage, as it enables the development of more efficient and compact hydrogen storage systems. This can have a major impact on the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology, which is considered a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Applications in carbon capture and storage
The new MOF synthesis method has significant implications for the development of affordable carbon scrubbers and advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies aim to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere by capturing and storing it in various forms. MOF-based CCS systems can play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions from industrial sources.
The enhanced gas capture capabilities of the new MOF crystals can be leveraged to develop more efficient carbon scrubbers, which can be integrated into power plants and industrial processes. This can significantly reduce the amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
Atmospheric water harvesting
In addition to carbon capture and storage, the new MOF synthesis method can also be applied to atmospheric water harvesting. This technology involves the use of MOFs to capture and condense water vapor from the air, providing a sustainable source of clean water. The high surface area and tunable properties of MOFs make them ideal for atmospheric water harvesting, as they can selectively trap water molecules and release them as liquid water.
The development of advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems can have a major impact on global water security, particularly in arid and water-scarce regions. By leveraging the enhanced gas capture capabilities of the new MOF crystals, these systems can provide a reliable and sustainable source of clean water, contributing to improved health and well-being.
Conclusion
The development of a fluoride-free synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks marks a significant breakthrough in the pursuit of clean energy and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. The new synthesis method simplifies the production process, reduces costs, and yields superior crystals with enhanced gas capture capabilities. The implications of this innovation are far-reaching, with potential applications in carbon capture and storage, atmospheric water harvesting, and hydrogen storage.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, the development of efficient and sustainable technologies is crucial. The new MOF synthesis method offers a promising solution, enabling the widespread adoption of MOF-based technologies and contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment. With further research and development, the potential of MOFs to combat climate change can be fully realized, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage