Safer method boosts gas capture for clean energy
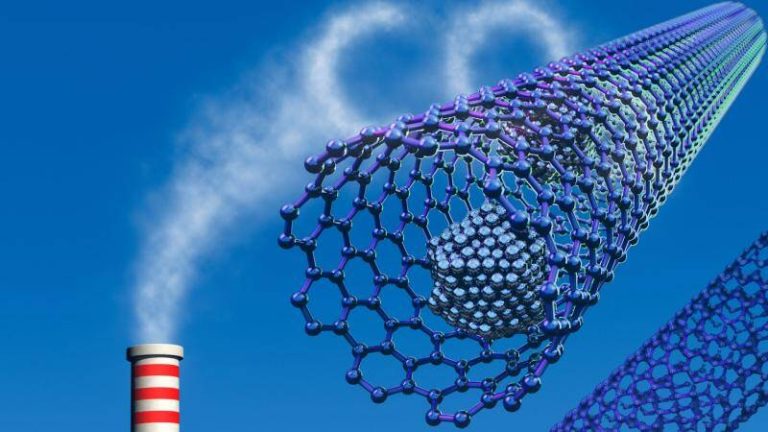
The pursuit of clean energy and reduced greenhouse gas emissions has been a longstanding goal for scientists and researchers worldwide. One crucial aspect of achieving this objective is the development of efficient methods for capturing and storing carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have emerged as promising materials for this purpose, owing to their unique structure and properties. However, the traditional synthesis of MOFs often involves the use of toxic hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant safety risks. In a groundbreaking breakthrough, researchers have developed a fluoride-free synthesis method for MOFs, replacing hydrofluoric acid with safer modulators. This innovative approach not only enhances the safety of the synthesis process but also yields superior crystals that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature.
The traditional method of synthesizing MOFs involves the use of hydrofluoric acid, a highly corrosive and toxic substance that requires specialized handling and equipment. The risks associated with hydrofluoric acid are well-documented, and its use has been a major concern for researchers and laboratory personnel. In contrast, the new fluoride-free synthesis method utilizes safer modulators, which not only reduce the risks associated with hydrofluoric acid but also simplify the synthesis process. This simplified method produces MOFs with superior crystal structures, which are essential for efficient gas capture and storage.
One of the most significant advantages of the new synthesis method is its ability to produce MOFs that can trap greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, more efficiently. The superior crystal structure of the MOFs synthesized using the fluoride-free method enables them to capture carbon dioxide at room temperature, which is a critical factor in the development of affordable carbon scrubbers. Carbon scrubbers are devices that can remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and their efficiency is crucial in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The new synthesis method paves the way for the development of more efficient carbon scrubbers, which can play a vital role in mitigating climate change.
In addition to capturing greenhouse gases, the MOFs synthesized using the fluoride-free method can also store hydrogen more efficiently. Hydrogen is a clean-burning fuel that can be used to power vehicles and generate electricity, and its storage is a critical aspect of its widespread adoption. The superior crystal structure of the MOFs enables them to store hydrogen at room temperature, which is a significant advantage over traditional hydrogen storage methods. This breakthrough has the potential to accelerate the development of hydrogen fuel cell technology, which can provide a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
The implications of the new synthesis method extend beyond the development of carbon scrubbers and hydrogen storage systems. The simplified and safer method can also facilitate the widespread adoption of MOFs in various applications, including advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems. These systems can provide clean drinking water for millions of people worldwide, particularly in areas where access to clean water is limited. The use of MOFs in atmospheric water harvesting systems can help to address the global water crisis, which is closely linked to climate change.
The development of the fluoride-free synthesis method is a testament to the power of scientific innovation and collaboration. The researchers involved in this breakthrough have demonstrated that it is possible to develop safer and more efficient methods for synthesizing MOFs, which can have a significant impact on the environment and human health. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, the development of more efficient and sustainable technologies is crucial. The new synthesis method for MOFs is a significant step in this direction, and its potential applications are vast and varied.
In conclusion, the development of a fluoride-free synthesis method for metal-organic frameworks is a groundbreaking breakthrough that has the potential to revolutionize the field of clean energy. The safer and more efficient method can produce superior crystals that can trap greenhouse gases and store hydrogen more efficiently at room temperature. The implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching, and its potential applications include the development of affordable carbon scrubbers, advanced atmospheric water harvesting systems, and more efficient hydrogen storage systems. As the world continues to pursue a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future, innovations like the fluoride-free synthesis method for MOFs will play a vital role in achieving this goal.
News Source: https://researchmatters.in/news/greener-path-synthesising-metal-organic-frameworks-carbon-capture-and-storage