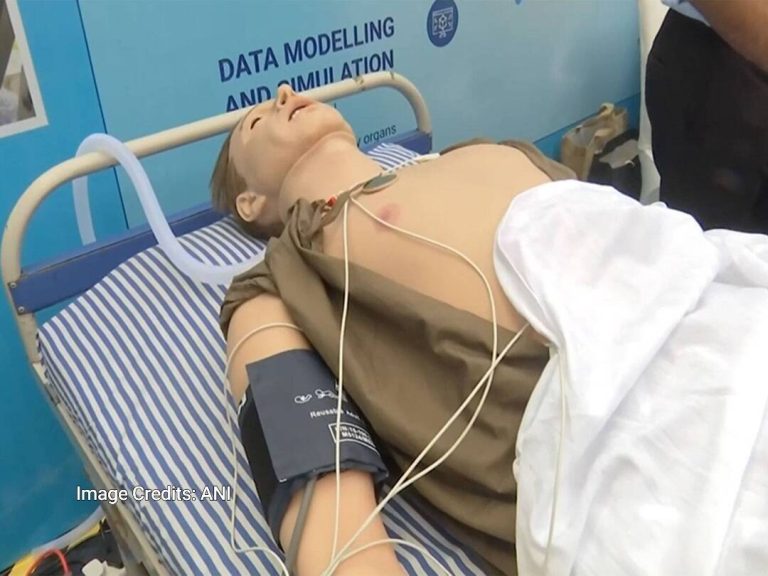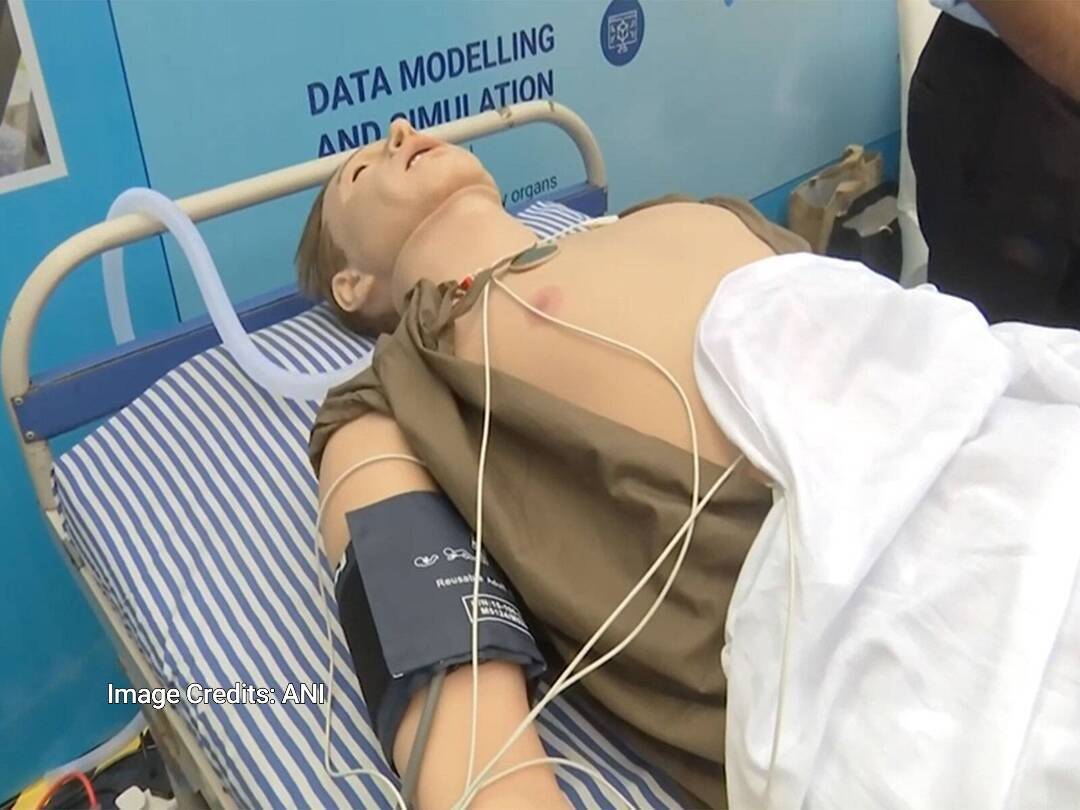
IIT Indore creates AI human replica to help detect diseases
In a groundbreaking development, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Indore has created an artificial intelligence (AI) powered human-like replica that can aid in the detection of diseases in the human body. According to a report by ANI, this innovative replica is capable of mimicking basic human functions such as blinking and breathing, making it an invaluable tool for medical professionals to identify patterns of diseases in various organs.
The AI-powered human replica is a significant breakthrough in the field of medical technology, and it has the potential to revolutionize the way diseases are diagnosed and treated. By replicating human functions, the AI robot can help doctors to better understand the progression of diseases and develop more effective treatment plans. The replica can also assist in the early and preventive diagnosis of diseases, which is critical for improving patient outcomes.
One of the most significant advantages of the AI-powered human replica is its ability to simulate human-like functions, making it an ideal tool for testing and training medical professionals. The replica can be used to simulate various scenarios, allowing doctors to practice and refine their skills in a realistic and risk-free environment. This can be particularly useful for training medical students and junior doctors, who can benefit from hands-on experience without putting real patients at risk.
The development of the AI-powered human replica is also a testament to the growing importance of artificial intelligence in healthcare. AI has the potential to transform the healthcare industry in numerous ways, from diagnosing diseases more accurately to developing personalized treatment plans. The use of AI-powered robots like the human replica can help to improve patient care, reduce costs, and enhance the overall efficiency of healthcare systems.
The AI-powered human replica can also be used to study the behavior of diseases in various organs and tissues. By simulating the progression of diseases, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms and develop more effective treatments. This can be particularly useful for studying complex diseases such as cancer, where the behavior of cancer cells can be simulated and analyzed in detail.
Another significant advantage of the AI-powered human replica is its ability to provide personalized medicine. By simulating the behavior of diseases in individual patients, doctors can develop personalized treatment plans that take into account the unique characteristics of each patient. This can lead to more effective treatment outcomes and improved patient care.
The development of the AI-powered human replica is a significant achievement for IIT Indore, which has established itself as a leading institution in the field of technology and innovation. The institute has a strong focus on research and development, and it has made significant contributions to various fields, including healthcare, robotics, and artificial intelligence.
In conclusion, the AI-powered human replica developed by IIT Indore is a groundbreaking innovation that has the potential to transform the field of healthcare. By simulating human-like functions and aiding in the detection of diseases, the replica can help doctors to develop more effective treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. The use of AI-powered robots like the human replica is a significant step forward in the field of medical technology, and it is likely to have a major impact on the way diseases are diagnosed and treated in the future.
As the field of artificial intelligence continues to evolve, we can expect to see more innovative applications of AI in healthcare. The development of AI-powered human replicas is just one example of the many ways in which AI can be used to improve patient care and outcomes. As researchers and developers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with AI, we can expect to see even more exciting innovations in the field of healthcare.