IIT Indore creates AI human replica to help detect diseases
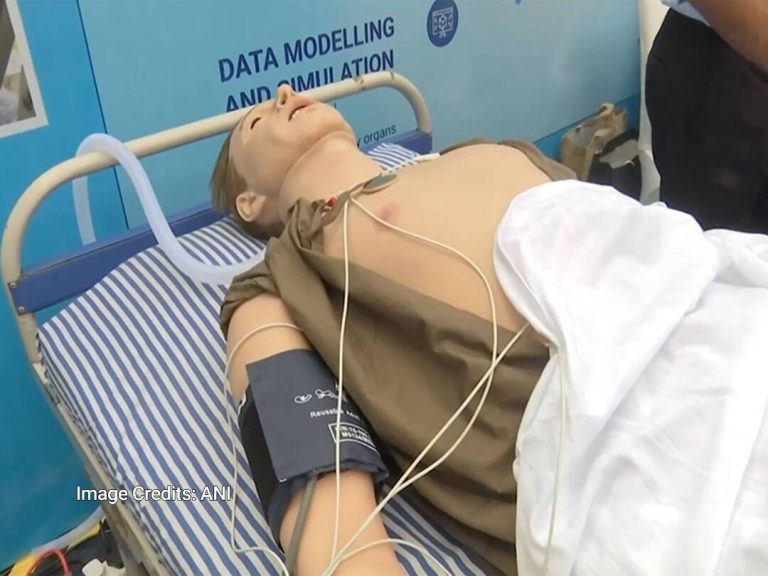
In a groundbreaking achievement, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Indore has developed an AI-powered human-like replica that can be used to detect diseases in the human body. This innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine by aiding doctors in early and preventive diagnosis. According to a report by ANI, the replica can imitate basic human functions like blinking and breathing, making it an incredibly realistic and useful tool for medical professionals.
The AI-powered human replica is equipped with advanced technology that allows it to simulate various human functions, including breathing, blinking, and even heart rate. This enables doctors to study the patterns of diseases in different organs and identify potential health risks before they become severe. The replica can be used to detect a wide range of diseases, from cardiovascular disorders to respiratory problems, and even neurological conditions.
One of the most significant advantages of this technology is its ability to aid in early diagnosis. By using the AI-powered human replica, doctors can identify disease patterns and detect potential health risks before symptoms become apparent. This can lead to earlier intervention and treatment, improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications. Additionally, the replica can be used to test new treatments and medications, allowing doctors to refine their approaches and develop more effective therapies.
The development of the AI-powered human replica is a testament to the innovative spirit of IIT Indore and its commitment to advancing the field of medicine. The institute has been at the forefront of research and development in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and healthcare technology, and this latest achievement is a significant milestone in its efforts to improve human health.
The use of AI in healthcare is not new, but the development of a human-like replica takes this technology to a whole new level. AI has been used in various medical applications, from diagnostic imaging to personalized medicine, but the creation of a realistic human replica is a game-changer. It allows doctors to interact with a simulated human body, studying disease patterns and testing treatments in a highly realistic and controlled environment.
The potential applications of this technology are vast and varied. For example, the AI-powered human replica could be used to train medical students, allowing them to practice and refine their skills in a safe and controlled environment. It could also be used to educate patients about their conditions, helping them to better understand their treatment options and make informed decisions about their care.
Furthermore, the AI-powered human replica could be used to develop more effective treatment plans, tailored to the individual needs of each patient. By simulating the behavior of diseases in different organs and systems, doctors can identify the most effective treatments and develop personalized therapy plans. This could lead to better patient outcomes, improved quality of life, and reduced healthcare costs.
In addition to its potential applications in medicine, the AI-powered human replica also raises important questions about the future of healthcare and the role of technology in patient care. As AI becomes increasingly integrated into healthcare, there will be a need for ongoing evaluation and assessment of its benefits and risks. This will require careful consideration of issues such as data privacy, patient consent, and the potential for bias in AI decision-making.
In conclusion, the development of the AI-powered human replica by IIT Indore is a significant achievement that has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine. By providing a realistic and interactive platform for doctors to study disease patterns and test treatments, this technology could lead to earlier diagnosis, improved patient outcomes, and reduced healthcare costs. As the use of AI in healthcare continues to evolve, it is essential to consider the potential benefits and risks of this technology and to ensure that it is developed and used in a responsible and ethical manner.