How Moon altered the orbit of Chandrayaan-3’s propulsion module?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved a significant milestone in its Chandrayaan-3 mission, with the spacecraft’s propulsion module undergoing a substantial change in its Earth orbit after passing close to the Moon. This alteration in the module’s orbit was made possible by the lunar gravity, which pulled the spacecraft during two flybys, one on November 6 and another on November 11, 2025. The ISRO has confirmed that this change in orbit was achieved without using any fuel, a remarkable feat that showcases the ingenuity and expertise of the Indian space agency.
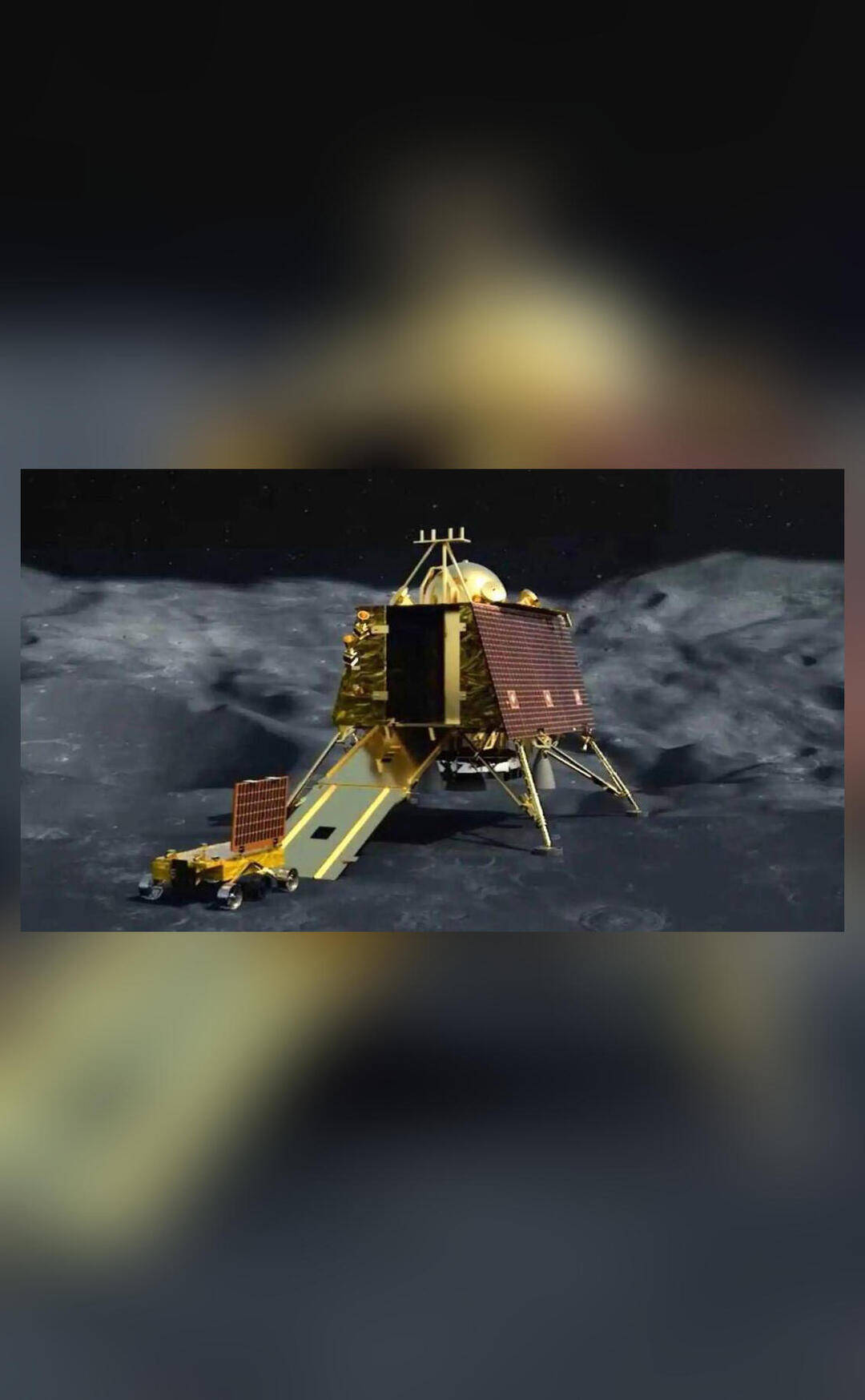
The Chandrayaan-3 mission, which was launched earlier this year, consists of a propulsion module, a lander, and a rover. The propulsion module is responsible for carrying the lander and rover to the Moon, where they will separate and descend to the lunar surface. The lander and rover are equipped with a range of scientific instruments designed to study the Moon’s surface, subsurface, and exosphere. The mission aims to expand our knowledge of the Moon and its resources, as well as to demonstrate key technologies required for future lunar and planetary missions.
The two flybys of the Moon by the propulsion module were a crucial part of the mission plan. During these flybys, the lunar gravity pulled the spacecraft, naturally altering its path without the need for any fuel. The first flyby, which occurred on November 6, saw the spacecraft pass within 3,740 km of the Moon’s surface. The second flyby, which took place on November 11, saw the spacecraft pass within 4,537 km of the lunar surface. These flybys were carefully planned and executed by the ISRO team, who used the lunar gravity to change the module’s orbit size and direction.
The change in orbit achieved by the ISRO is a significant accomplishment, as it demonstrates the agency’s ability to use gravitational forces to alter the trajectory of a spacecraft. This technique, known as gravity assist, has been used by space agencies around the world to send spacecraft to distant planets and moons. However, the use of gravity assist to alter the orbit of a spacecraft in Earth orbit is a more complex and challenging task, requiring precise planning and execution.
The ISRO has stated that the change in orbit achieved by the Chandrayaan-3 propulsion module will help to reduce the amount of fuel required for future maneuvers. This is because the new orbit will allow the spacecraft to take advantage of the gravitational forces of the Earth and Moon, reducing the need for propulsive maneuvers. The agency has also confirmed that the lander and rover are functioning normally and are ready to separate from the propulsion module and descend to the lunar surface.
The success of the Chandrayaan-3 mission is a testament to the capabilities and expertise of the ISRO. The agency has a long history of achieving significant milestones in space exploration, including the successful landing of the Vikram lander on the Moon’s south pole during the Chandrayaan-2 mission. The Chandrayaan-3 mission is expected to build on this success, providing new insights into the Moon and its resources, and demonstrating key technologies required for future lunar and planetary missions.
In conclusion, the alteration of the Chandrayaan-3 propulsion module’s orbit by the Moon’s gravity is a significant achievement that demonstrates the ingenuity and expertise of the ISRO. The use of gravity assist to change the module’s orbit size and direction is a complex and challenging task, requiring precise planning and execution. The success of this maneuver is a testament to the capabilities of the ISRO and its ability to achieve significant milestones in space exploration.
For more information on this story, please visit: https://www.newsbytesapp.com/news/science/how-chandrayaan-3-propulsion-module-s-orbit-was-altered-by-moon-s-gravity/story