Asia’s Largest Undersea Gold Deposit Discovered
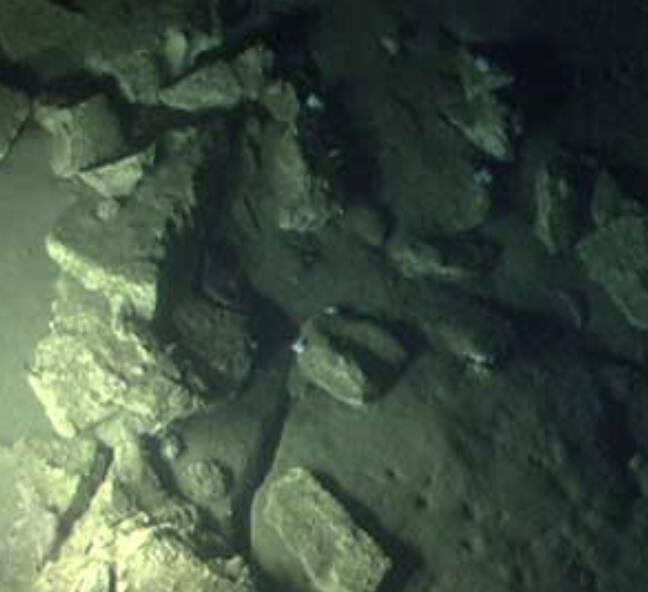
In a groundbreaking discovery, China has unearthed its first undersea gold deposit, which is also the largest in Asia, off the coast of Laizhou, in Yantai, Shandong province. This remarkable find has sent shockwaves of excitement throughout the mining industry, as it is expected to significantly boost China’s already impressive gold reserves. The discovery has lifted Laizhou’s total proven gold reserves to more than 3,900 tonnes, cementing China’s position as the world’s largest producer of gold ore.
The undersea gold deposit, located in the coastal waters of Laizhou, is a game-changer for China’s mining industry. The country has been actively exploring its territorial waters for mineral deposits, and this discovery is a testament to its efforts. The gold deposit is estimated to be vast, with initial reports suggesting that it could be the largest in Asia. This find is not only significant for China but also for the global mining industry, as it highlights the vast potential of undersea mining.
China’s gold production has been on the rise in recent years, with the country producing 377 tonnes of gold ore in 2020. This makes China the world’s largest producer of gold ore, accounting for a significant percentage of global production. The discovery of the undersea gold deposit is expected to further increase China’s gold production, solidifying its position as a major player in the global gold market.
The discovery of the undersea gold deposit has also lifted Laizhou’s total proven gold reserves to more than 3,900 tonnes. This is a significant increase from previous estimates, and it highlights the vast potential of the region’s gold deposits. Laizhou has long been known for its rich gold deposits, and this discovery is expected to attract more investment to the region. The increased gold reserves will also provide a boost to the local economy, creating new job opportunities and stimulating economic growth.
The undersea gold deposit is not only significant for its size but also for its potential to provide a new source of gold for China. The country has been actively seeking to diversify its gold sources, and this discovery provides a new avenue for gold production. The deposit is also expected to be more environmentally friendly than traditional gold mining methods, as it eliminates the need for deforestation and other habitat destruction.
The discovery of the undersea gold deposit is a result of China’s efforts to explore its territorial waters for mineral deposits. The country has been investing heavily in marine exploration and mining technology, and this discovery is a testament to its efforts. The use of advanced technology, such as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), has enabled China to explore its territorial waters more efficiently and effectively.
The implications of this discovery are far-reaching, and it is expected to have a significant impact on the global gold market. The increased gold production from China is likely to affect global gold prices, and it may also lead to changes in the global gold trade. The discovery of the undersea gold deposit is also expected to attract more investment to the region, as companies seek to capitalize on the new gold reserves.
In conclusion, the discovery of Asia’s largest undersea gold deposit off the coast of Laizhou, in Yantai, Shandong province, is a significant find that is expected to have a major impact on the global gold market. The increased gold reserves and production are likely to solidify China’s position as the world’s largest producer of gold ore, and it may also lead to changes in the global gold trade. As the mining industry continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how this discovery shapes the future of gold production and trade.